CSIC and the University of Santiago de Compostela have developed a new method that allows to detect the presence of ciliates that cause scuticociliatosis in flat fishes through a non-invasive method and even in low concentrations, facilitating the application of prevention and/or control measures in early stages of the infection, being therefore of high interest in aquaculture of high economic value species such as turbot and sole.
Industrial partners from the pharmaceutical or aquaculture industry are being sought to collaborate through a patent licence agreement to incorporate the process as a diagnosis product or service.
An offer for Patent Licensing
Effective and efficient monitoring of ciliates in fish farms
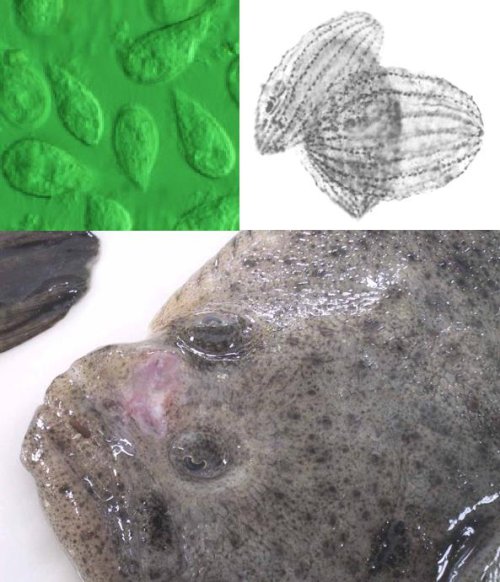
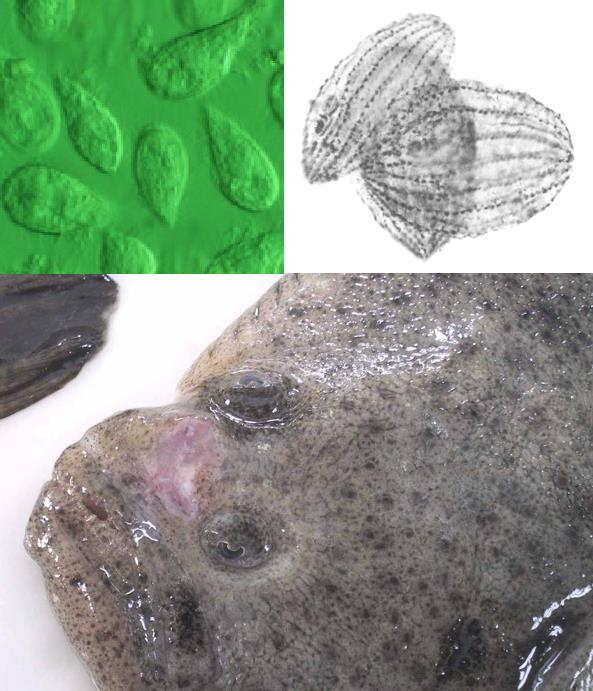
On the top, images of the ciliates that cause the scuticociliatosis. On the bottom, a turbot affected by the disease. Scuticociliatosis is one of the most relevant causes of mortality in flat fish farms, and presents a high potential of spread between individuals in tanks. Our new invention allows detecting the presence and concentration of the species of ciliates P. dicentrarchi and M. avidus very effectively, therefore allowing for a quantitative determination of the risk of infection or spread in a specific tank, and facilitating the application of preventive or control measures that can minimize economic and productive impacts in farms.
The method uses PCR amplification in order to detect the presence of the specific genetic material of these ciliates, what guarantees a high degree of precision (specificity) and a very low detection threshold. The samples used for the analysis can proceed both from the tank water and from tissues or fluids from individuals, therefore avoiding the need to sacrifice individuals for the analysis.
Main innovations and advantages
Its main applications correspond to the field of fish farming, for farmsspecialized in flat fishes. Its main advantages include:
· Allows for an effective and efficient monitoring of the presence ofparasite ciliates both in water tanks and in individuals.
· The sampling process from individuals can be done without usinginvasive methods or sacrifice.
· The detection threshold for the ciliates is very low.
· Allows obtaining results in a few hours after the sampling.