New digital photomultiplier with spatial filtering of spurious avalanches, adjustable dead-time and reduced power consumption
Conventional silicon photomultipliers (SiPM) allow the development of avalanche currents at their maximum amplitude, thus generating current intensities of considerable magnitude. In addition to this, and due to the recharge through a resistor, the reload times are quite long. This causes extraordinary energy expenditure and the device is unused for an excessively long period of time.
On the other hand, digital silicon photomultipliers (d-SiPM) partially solve the problems mentioned, but this is achieved thanks to the reduction of the fill factor (FF), which causes a loss of sensitivity. Likewise, this architecture also produces unnecessary power consumption, introduced by the avalanches that are generated within the dead-time.
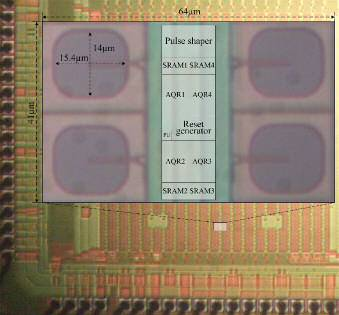
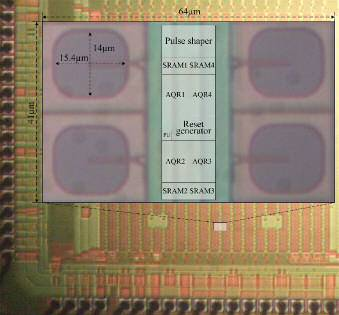
The proposed digital OR pulse combining photomultiplier solves these problems by associating N microcells in the same macrocell. The N photodiodes in each macrocell are deactivated together during the dead-time that elapses after the triggering of an avalanche in only one of them. Here it is the key to greater energy efficiency, in the fact that an avalanche in one of the SPADs prevents the rest of the macrocells from firing. This developed photomultiplier makes it possible to increase the fill factor, reduce noise and regulate dead-time.
Microfotography of a macro-cell contains 4 microcells that share circuitry.
Main innovations and advantages
· It is a photomultiplier where a first detection automatically disables the rest of the microcells.
· The rest of the detections that occur after the first one are masked with the OR-combination scheme, allowing energy savings.
· The use of PMOS transistors is avoided allowing a significant improvement in fill factor · FF).