cyber-physical system CSIC and Universidad Politécnica de Madrid have developed an intelligent connectable device for the automatic parameterization of controllers of a physical and cybernetic system. This device has a new procedure designed to automatically parameterize the physical system controller. For this, it relies on a simulation in parallel and in real time of both the physical system model and the controller (digital twin).
Industrial partners are being sought to collaborate through a patent licence agreement.
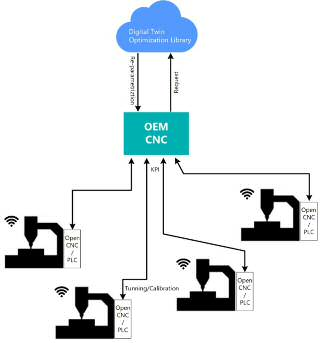
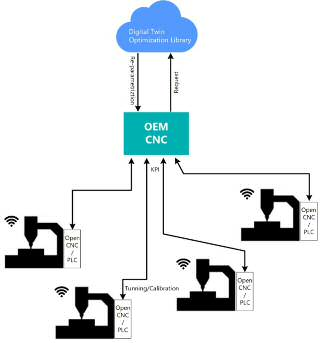
Digital twin for automatic parameterization.
Today's tracking and positioning systems require very precise controllers. Currently, there are limitations in the scope and optimal operation of controllers adjusted or tuned by manual and/or experimental parameterization, specifically due to the cross-correlation of the parameters and the cross-influence of the control parameters and the anticipatory components in the presence of hard nonlinearities like friction and backlash The proposed procedure is mainly composed of two steps: 1. Generation of digital twin of the cyber-physical system (physical system connected to the network). 2. Determination of the value of the optimal controller parameters To carry out the optimization process, three gradient-free heuristic methods are used: simulated annealing (SA), genetic algorithm (GA, Genetic Algorithm), and cross-entropy (CE, Cross-Entropy). The method of the present invention applies one of these heuristic optimization methods, in combination with the generated digital twin, to obtain the optimal value of the controller parameters that minimizes the chosen cost function.
Diagram of optimization approach based in Digital Twin The digital twin is configured using the characteristic parameters of the machine tool.
Main innovations and advantages
· The procedure of the present invention makes it possible to optimize in an automated way and without the need for empirical tests (as it occurs in currently known methods) the characteristic parameters of the controller of a physical system, · Reduces set-up and calibration costs.
· It allows updating the controller located in a remote place only from the knowledge of its characteristic parameters from the digital twin.
· Improves the precision of the control system · It has applications for the manufacturers of motors and their regulation systems, as well as in the equipment or machinery that are used in positioning · For example, in the manufacturing industry, specifically in the processes of machining parts using numerically controlled · CNC) machines.