Disease CSIC, Université de Lille, INSERM and Centre Hospitalier Regional Universitaire de Lille have developed an in vitro method for designing a customized therapy for a Parkinson ‘s Disease patient through the determination of the presence of a centrosomal deficit from that subject and therefore susceptible to receive a therapy based on a LRRK2 inhibitor. LRRK2 is a key player for the development of both genetic and sporadic forms of Parkinson’s Disease (PD).
Industrial partners from pharmaceutical industry are being sought to collaborate through a patent licence agreement.
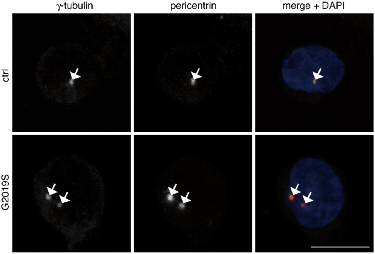
Centrosomal cohesion deficit as biomarker for PD We have demonstrated that determination of a centrosomal deficit serves as a convenient and robust cellular biomarker for the detection of LRRK2 alterations in patients with or without LRRK2 mutations, which can be reverted by a LRRK2 kinase inhibitor. This assay may serve as a cellular readout for screening novel LRRK2 kinase inhibitors. Our results also suggest that this cellular marker may have added value in the early detection and prediction of PD (in combination with detailed neurologial examinations), and in determining the biological activity of LRRK2. Centrosomal deficit in lymphoblastoid cell line from LRRK2-PD patient (G2019S) but not healthy control patient. From Fernández et al., Biochem. J., 2019.
Main innovations and advantages
· The absence of early biological markers for PD hampers the development of efficient neuroprotective drug testing approaches.
Here, we propose the detection of a centrosomal cohesion deficit as a tool which will enable:
early detection of pathophysiology enabling large-scale controlled multi-center trials
patient stratification purposes to identify patients who may also benefit from validated · LRRK2 inhibitor approaches
tracking of disease-modifying pharmacological effects in the context of translating a validated · LRRK2 kinase inhibitor into clinical settings
assessment of objective treatment benefits such that the therapeutic regime can be adjusted according to patient response · Determination of centrosomal cohesion deficits can be performed in peripheral patient-derived cells, and correlated to · LRRK2, Ser935LRRK2, phospho-Rab10 and Rab10 levels in comparison to a validated LRRK2 inhibitor compound as positive control, when analysing your own kinase inhibitors/compounds targeting · LRRK2.