Never miss an update from Javier Montiel Bonmatí
Create your free account to connect with Javier Montiel Bonmatí and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
The "Molecular Microbiology" research group at the University of Alicante has modified several phage proteins (Poll-N and UK-C) that have high specificity against Escherichia coli (E. coli), but not against other Gram-negative (G-) bacteria.
For these reasons, their use as a specific antimicrobial against E. coli is potentially interesting, especially in the case of contaminated food, cosmetics or water. It would also be useful in the treatment of diseases (infections) caused by E. coli.
The presence of a histidine tail attached to the phage proteins not only facilitates their purification but also improves lysis efficiency without the need of cell permeabilization treatments.
Companies interested in the commercial exploitation of the technology through license agreements and/or technical cooperation are sought.
The "Molecular Microbiology" research group at the University of Alicante has developed several modified phage proteins (Poll-N and UK-C) with antibacterial activity highly specific against E. coli without the need for previous permeabilization treatments.
Polypeptides (proteins) are a sequence of amino acids that are joined together by peptide bonds.
The polypeptides developed with endolysin activity, Poll-N and UK-C, comprise, respectively:
• An amino acid sequence according to SEQ ID NO: 3, or a derivative thereof (deletion, addition, insertion and/or substitution in this amino acid sequence), and a polycationic tail of amino acids (histidines) at the N-terminal end; and,
• An amino acid sequence according to SEQ ID NO: 4, or a derivative thereof (deletion, addition, insertion and/or substitution in this amino acid sequence), and a polycationic tail of amino acids (histidines) at the C-terminal end.
Once cloned, expressed and purified, the resulting proteins (Poll-N and UK-C) carry a histidine tail at their N-terminal or C-terminal end, being therefore different from the original. This tail not only facilitates its purification, but also favors the endolysin contact to the cell surface, thus improving its lysis efficiency.
The developed polypeptides can be used both as antimicrobial agents to prevent contamination by E. coli and in the treatment of diseases (infections) produced by E. coli.
MAIN ADVANTAGES OF THE TECHNOLOGY
The main advantages of the synthesized peptides, Poll-N and UK-C, are the following:
INNOVATIVE ASPECTS OF THE TECHNOLOGY
The main innovative aspect of the modified phage proteins is that they do not require prior treatments of OM permeabilization. Furthermore, the addition of nucleotides at the ends facilitates their manipulation and subsequent cloning in the appropriate expression vector. Finally, another innovative aspect is the generation of anti-E. coli endolysins whose sequence is significantly different from others.
CURRENT STATE OF DEVELOPMENT
The technology is developed at laboratory scale.
The efficacies of purified Poll-N and UK-C endolysins have been tested by means of spot test experiments against different bacterial strains. Figure 1 (for Poll-N) and Figure 2 (for UK-C) show the appearance of growth inhibition zones produced by lysis.
The results obtained show that both Poll-N and UK-C are capable of directly lysing the majority (92.5% for Poll-N and 91.2% for UK-C) of E. coli strains tested (159 in total).
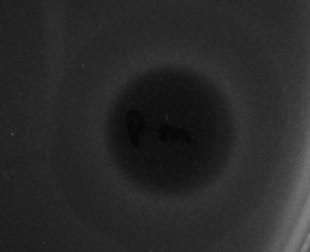
Figure 1. Result of a spot test experiment carried out with Poll-N at a concentration of 16 µg/mL on an E. coli strain. Bacterial growth is visualized as a gray layer on the plate. The dark central area, where the protein solution was loaded, indicates the inhibitory effect in growth produced by the endolysin.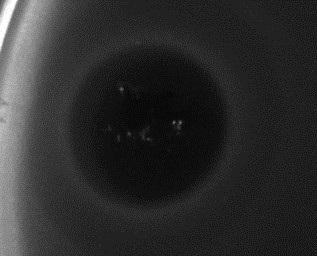
Figure 2. Result of a spot test experiment carried out with UK-C at a concentration of 16 µg/mL on an E. coli strain. Bacterial growth is visualized as a gray layer on the plate. The dark central area, where the protein solution was loaded, indicates the inhibitory effect in growth produced by the endolysin.
MARKET APPLICATION
The present invention is framed in the general field of genetic engineering and, in particular, it refers to viral proteins that have been modified by means of the addition of a polycationic tail of amino acids at the N-terminal or C-terminal end, in such a way that they present antibacterial activity against E. coli without previous treatments of envelope permeabilization. Both proteins show a high specificity to E. coli.
Therefore, the developed polypeptides can be used both as antimicrobial agents against E. coli (particularly in food, cosmetics, water contaminated with E. coli, etc.), as well as in the treatment of diseases (infections) produced by E. coli.
This technology could be applied in biosanitary, veterinary, biotechnological, or agri-food companies interested in antimicrobial treatments alternative to antibiotics to control the growth of E. coli.
COLLABORATION SOUGHT
Companies interested in acquiring this technology for its commercial exploitation through technology transfer agreements (see below) are sought:
Type of company sought:
Ahead of the current Coronavirus outbreak, Innoget is fully committed to contributing to mobilizing scientific and expert communities to find a real solution to the Covid-19 pandemic. Therefore, we're supporting worldwide calls and programs that could help in any aspects of the coronavirus crisis.
Is your organization promoting or looking for innovation or research initiatives to mitigate the Covid-19 outbreak? Email us at covid19@innoget.com to list them.
Channeled through Innoget's online open innovation network, initiatives in the health, virology, medicine, or novel technologies applied to human health, among others, are listed and disseminated to Innoget members -ranging from hospitals, research institutes, scientists, businesses, and public administrations- and innovation partners worldwide.
Create your free account to connect with Javier Montiel Bonmatí and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
Send a request for information
to Javier
Technology Offers on Innoget are directly posted
and managed by its members as well as evaluation of requests for information. Innoget is the trusted open innovation and science network aimed at directly connect industry needs with professionals online.
Need help requesting additional information or have questions regarding this Technology Offer?
Contact Innoget support