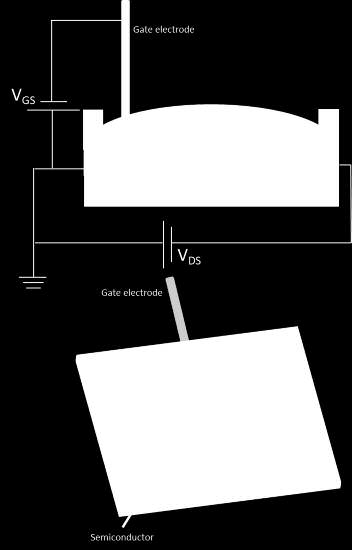
CSIC has developed a resistive thermal source suitable for thin layer deposition by Physical Vapor
Deposition. Deposition can be optimized with the new sources since they admit more than twice the
evaporant mass compared with conventional sources consisting in helical filaments of the same length
and at the same electric power. This new source has a simple geometry which makes fabrication easier
and lowers its costs
Industrial partners manufacturers of lab equipment are being sought to collaborate through a patent
license agreement.
An offer for Patent Licensing
A simplified design with improved performance
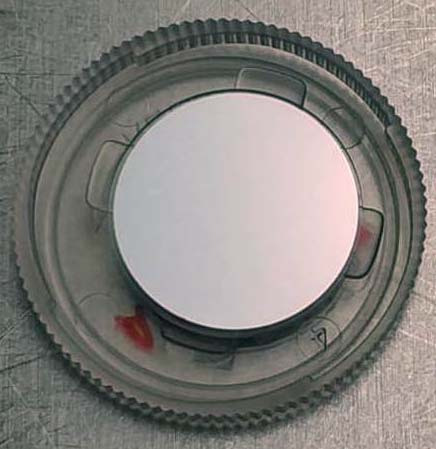
Ultraviolet filter type surface of a part after being coated using the developed thermal source Currently, for thin layer production by PVD, helical filaments are used as thermal resistive sources. This type of sources can be loaded with a limited mass of the material to be evaporated, which demands a higher number of sources and/or a high replacement frequency.
The thermal resistive source developed by CSIC consists in an arrangement of refractory-metal wires with a configuration and a geometry that allows a higher efficiency of evaporation process. This multifilament source accepts a higher load of the material to be evaporated and at the same time enhances emission in 30% to 60% per unit of evaporated mass with regard to sources based on helical filaments.
Main innovations and advantages
· The source admits higher loads of the material to be evaporated incomparison to conventional sources.
· The source presents higher emission efficiency and easier regulation ofthe evaporation temperature than conventional sources.
· Manufacturing process is simpler and less expensive than forconventional sources with helical filaments since the new source has asimple geometry allowing a reduction in the resistive material needed.
· A safe and simple placement of the material to be evaporated.
· Its scalable design makes it adaptable to the dimension of any vacuumchamber or to the thickness of the layer to be deposited.
· Suitable for the deposition of a wide variety of materials in both highvacuum and ultra-high vacuum.