CSIC has developed a new system that allows to identify and classify nanometric and micrometric
particles. This system is based on the changes produced at different resonance frequencies of thin plate
type structures when these particles are adsorbed onto their surface. This technology represents an
important achievement in the field of nanomechanical spectrometry and is suitable for the
identification and classification of viruses, bacteria or proteins.
Industrial partners manufacturers of lab equipment are being sought to collaborate through a patent
license agreement.
An offer for Patent Licensing
An alternative to atomic force microscopy and a very useful
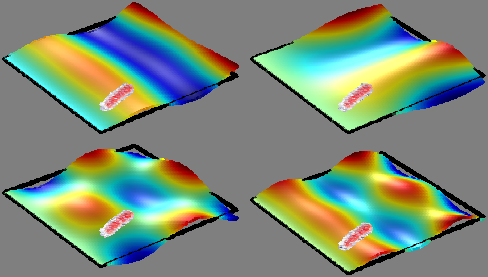
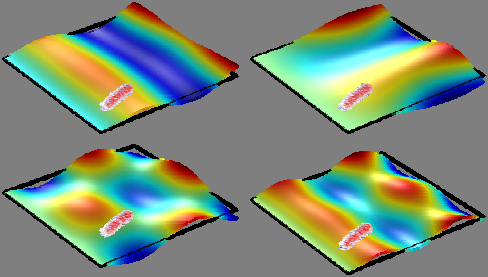
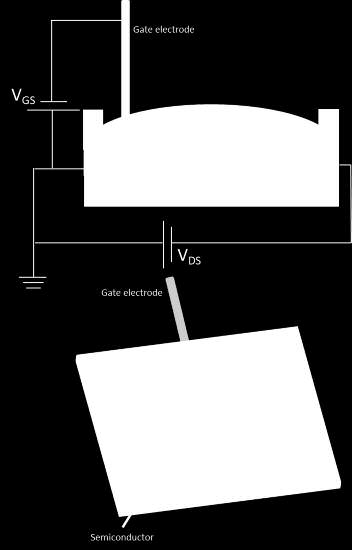
complement to conventional mass spectrometry Nanomechanical spectrum Identification When characterizing a sample, to determine the stiffness is very useful since this property is related to its internal structure and composition. In particular, in mass spectrometry (MS) techniques, the possibility to provide information about the stiffness represents a potential improvement. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) is the most commonly used technique to measure the stiffness of micro and nanoparticles. However, this technique is time- consuming and really invasive.
The system developed by CSIC provides a simple, reliable, fast and non- invasive method to identify and classify particles. The method is based on frequency change of different modes of vibration of a plate due to the mass and stiffness of the particle adsorbed onto it. Due to the special characteristics of these resonant structures, particles with the same mass and Young's modulus but different shape can be distinguished. This is not possible with current methods using resonance frequency changes of one- dimensional resonators.
Main innovations and advantages
· It’s a high precision, non-invasive and faster method in comparison toAFM.
· It allows to identify and classify viruses, bacteria and/or cells, what isnot possible with conventional spectrometry. This represents animportant improvement with regard to current methods.
· It allows to distinguish particles with the same mass and Young'smodulus but different shape what is not possible with methods thatuses the changes in the resonance frequencies of one-dimensionalresonators.