The CSIC and IRYCIS (Ramón y Cajal Institute for Health Research) have developed a group of
compounds. These compounds have the ability to regulate the number of synapses that are formed
between neurons, as well as the probability that neurotransmitters are released from these, because
they have the capability of modulate the interactions that take place between the regulatory proteins
NCS-1 and Ric8a that regulate these two independent processes. Due to these neuromodulatory
properties, these compounds are useful for the treatment of neurological diseases as Alzheimer's
disease, Huntington or Parkinson's diseases among others.
Industrial partners from the ophthalmic or pharmaceutical industry are being sought to collaborate
through a patent license agreement.
An offer for Patent Licensing
Fighting the effects of neurological diseases using chemical
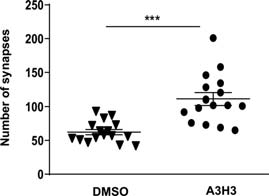
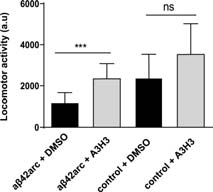
compounds that increase the numbers of synapsis Figure 1. The pathological reduction in the number of synapses was significantly reduced in the Drosophilas fed with A3H3 The proteins NCS-1 and Ric8a interact forming protein complexes that are fundamental for the formation of synapses and the release of neurotransmitters from these ones. Our chemical compounds, which have a structural nucleus of acylhydrazone, facilitate and stabilize the formation of this protein complex with dual function. It has been tested in different neurodegenerative models of Alzheimer in Drosophila, that the supply of these compounds in the diet, restore the number of synapses (see Figure 1) and the motor activity is fully recovered (Figure 2). Due to the very high conservation of the mechanisms and regulatory proteins of these processes between Drosophila and mammals, very promising results are expected in the treatment of neurological diseases in humans such as Alzheimer, Huntington or Parkinson with these compounds, where there is a drastic reduction in the number of synapses and in the release of neurotransmitters.
Main innovations and advantages
Figure 2. The locomotor deficit was complete-ly eliminated by feeding with A3H3 the flies.
· No other compounds have been described that increase the number ofsynapses through the NC1 / Ric8a complex.
· The regulation of the NC1 / Ris8a complex is fundamental due to itsdual role on the number of synapses and the release ofneurotransmitters, which very significantly increases the potential ofthese compounds as a therapeutic agent in long-term treatments ofneurological diseases.
· There are high expectations that these compounds will serve aspharmacological agents for the treatment of neurological diseasesproduce by the reduction in the number of synapses andneurotransmitters released.