CSIC has synthesized a series of piperidine derivatives that are capable of inhibiting the activity of the
enzyme phosphodiesterase-8 (PDE8). This inhibitory activity makes them useful for the treatment of
neurodegenerative diseases in which this enzyme is overexpressed. The compounds developed are,
therefore, a new therapeutic alternative for Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson, among others.
Industrial partners from pharmaceutical industry are being sought to develop and commercialized the
compounds through a patent licence agreement.
An offer for Patent Licensing
Control of neurodegenerative diseases
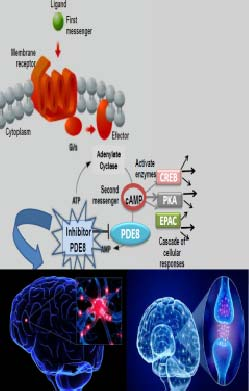
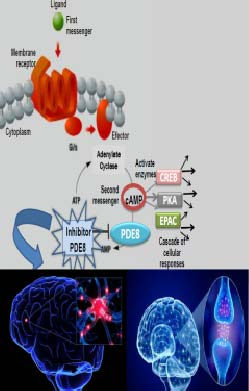
Given the difficulty in finding an effective treatment against neurodegenerative diseases, the search for new molecules that have viable pharmacological activity is a priority objective in the research on these pathologies Phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are the only enzymes that hydrolyze the cyclic nucleotides, cyclic guanosine monophosphate and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cGMP and cAMP). These nucleotides mediate the response of cells to a wide variety of hormones and neurotransmitters modulating many metabolic processes. That is why PDEs play crucial roles in the physiological processes that involve the signaling pathway of these nucleotides. Phosphodiesterase-8 (PDE8) is a cAMP-specific enzyme involved in many biological processes, including T-cell activation, testosterone production, adrenocortical hyperplasia and thyroid function, as well as neurodegenerative processes..
The new synthesized compounds, piperidine derivatives, are inhibitors of the PDE8A enzyme, in micromolar order, and are potential drugs for treatment and prevention of diseases in which this enzyme is overexpressed, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Main innovations and advantages
· They are able to cross the blood brain barrier, which is an additionaladvantage of the compounds when used in therapeutic treatments ofdiseases related to the central nervous system, such asneurodegenerative and / or neurological diseases.
· They can be presented in the most suitable pharmaceutical formulationfor each treatment.