Never miss an update from Servei de Gestió de la Innovació
Create your free account to connect with Servei de Gestió de la Innovació and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
We have developed a new algorithm for ordering anterior chamber OCT images in such a way that it is possible to classify them, in a fully unsupervised manner, in meaningful groups according to relevant features. We have tested the algorithm with a large set of images classified by two expert ophthalmologists, and with a larger set of annotated images. We have verified that the separation in the different classes defined by the ophthalmologists (closed, narrow, open, and wide open_ figure 6) is similar when using the manually extracted features, or when using the features that are returned by the unsupervised algorithm (View figures).
Therefore, the abstract features generated by the algorithm provide novel tools for assessing OCT images of the anterior chamber. They can be used for direct classification of the images and, furthermore, they can be linked to established quantities used for characterizing diseased eyes (like chamber depth, iris-corneal angle) resulting in an automatic detection system. As the algorithm is fully unsupervised, it can be easily automated and set up in OCT imaging systems to aid technicians and doctors in an early diagnosis. The two main advantages of the algorithm demonstrated here over previous works are that it doesn’t need any ground truth or gold standard for training, and it does not rely on specific landmarks; thus, it can analyze images in which relevant landmarks are not visible or not easy to locate.
The outcome of the algorithm applied to the image database is presented in the
way of an “Image Map”. A regular grid in the coordinates space (w, v) is defined and one image per grid point is
displayed.
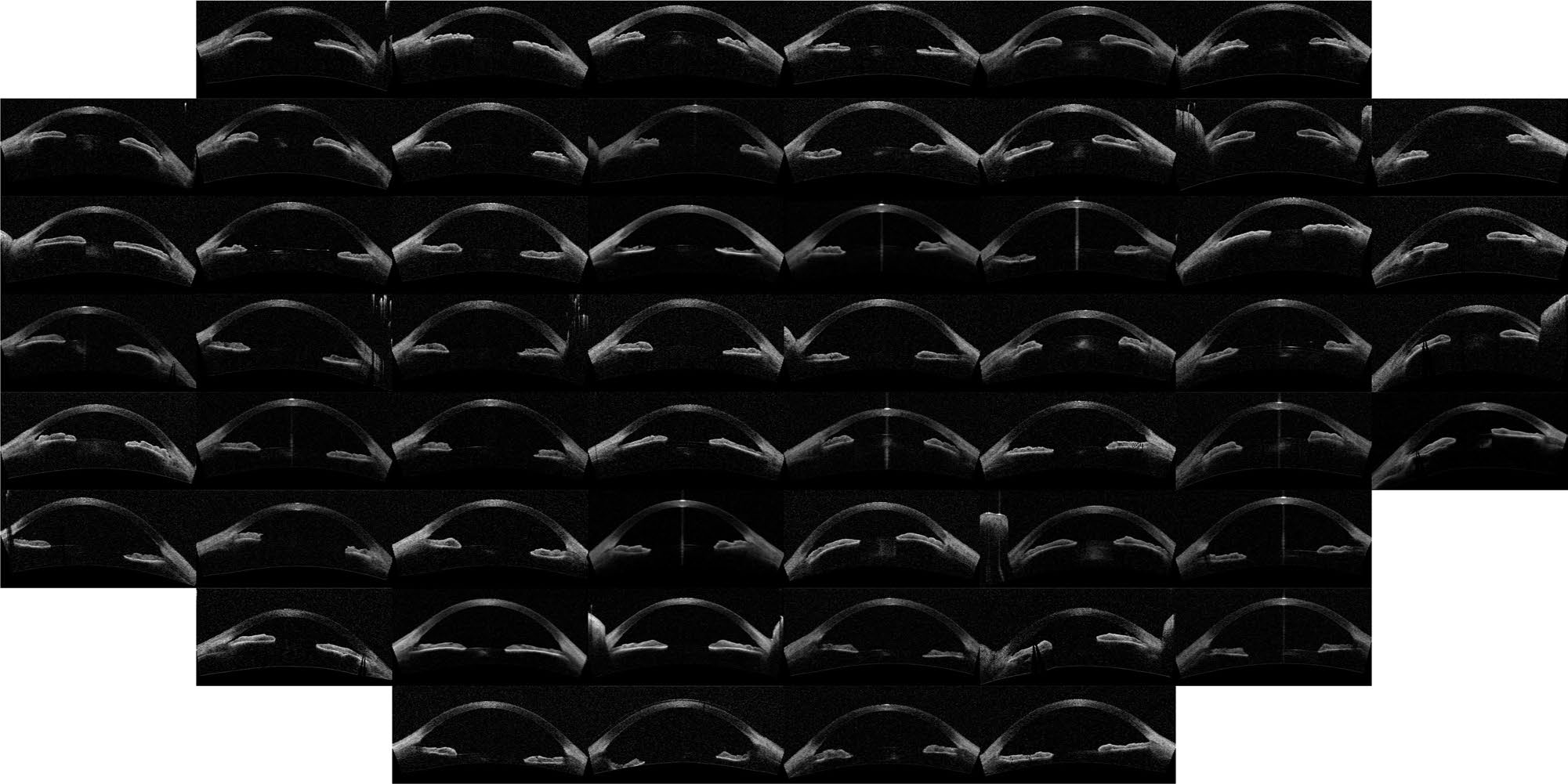
In Fig. 1 (IsoMap with Euclidean distance) it is apparent that the algorithm ordered the images according to the orientation (horizontal axis) and position (vertical axis) of each eye inside the OCT image, which are irrelevant
features, this simple algorithm is, then, not capable of extracting useful features. However, when including
the alignment step in the pre-processing of the images which removed the variability detected by the first algorithm,
meaningful features were extracted, as it can be seen in the Image Map in Fig. 2 (these features correlate
with the features derived manually,).
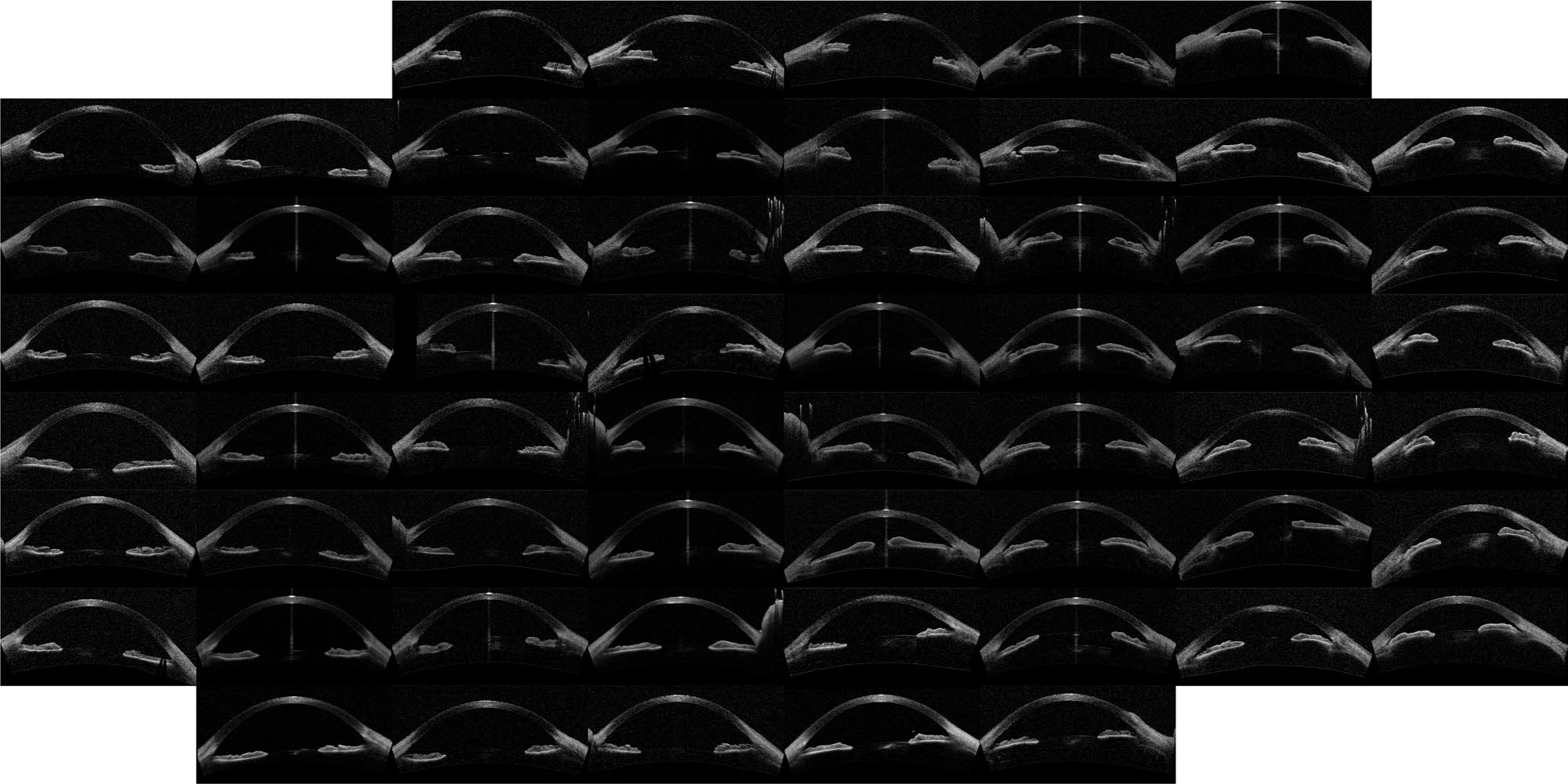
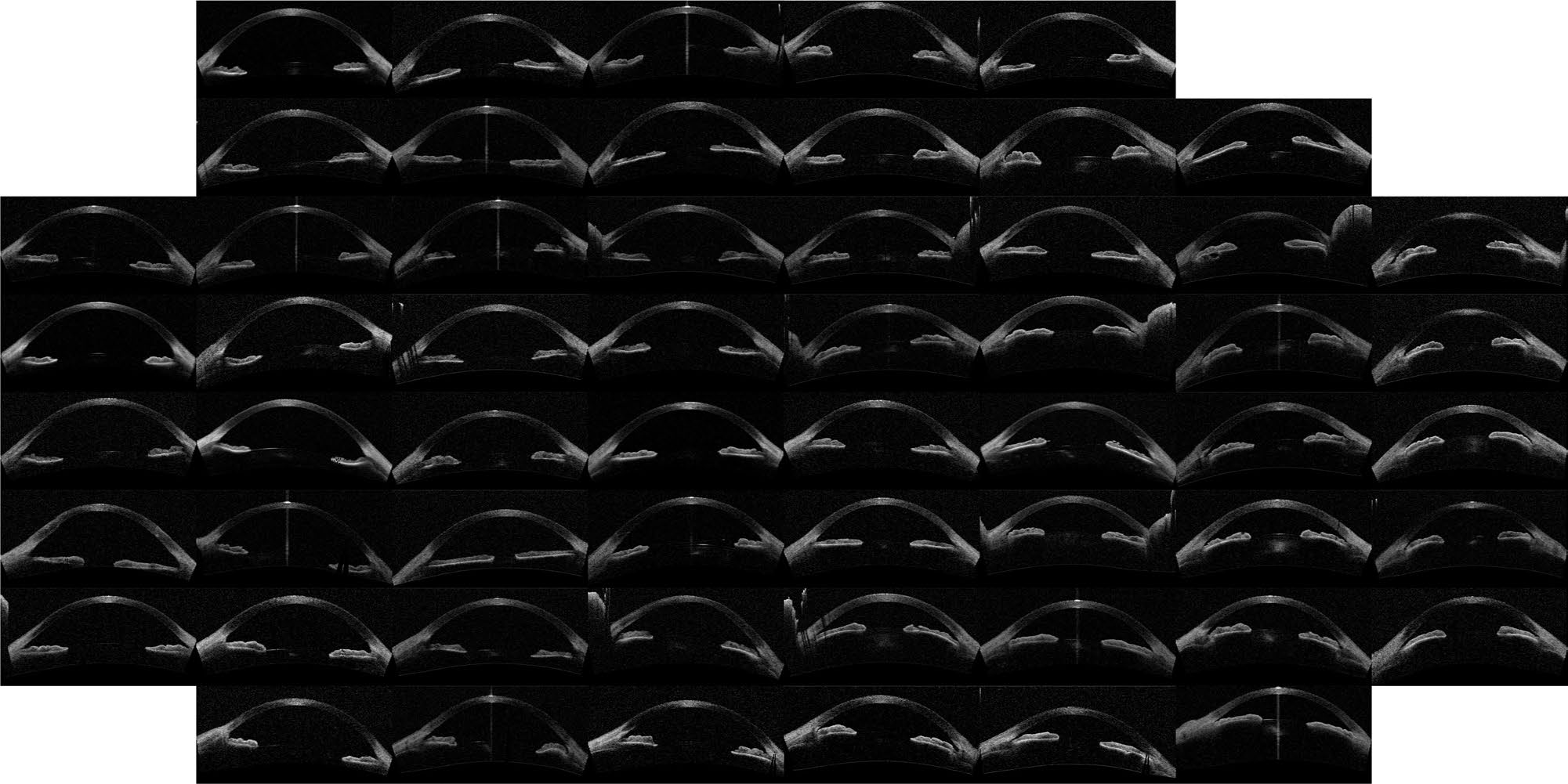
A similar map was obtained with the Hellinger distance shown in Fig. 3( see below) which marginally improves the performance with the Euclidean distance. To test the robustness to of the image ordering, the t-SNE algorithm was applied (instead of IsoMap).

The map obtained is shown in Fig. 4 (below) which turned out to perform slightly better than IsoMap.
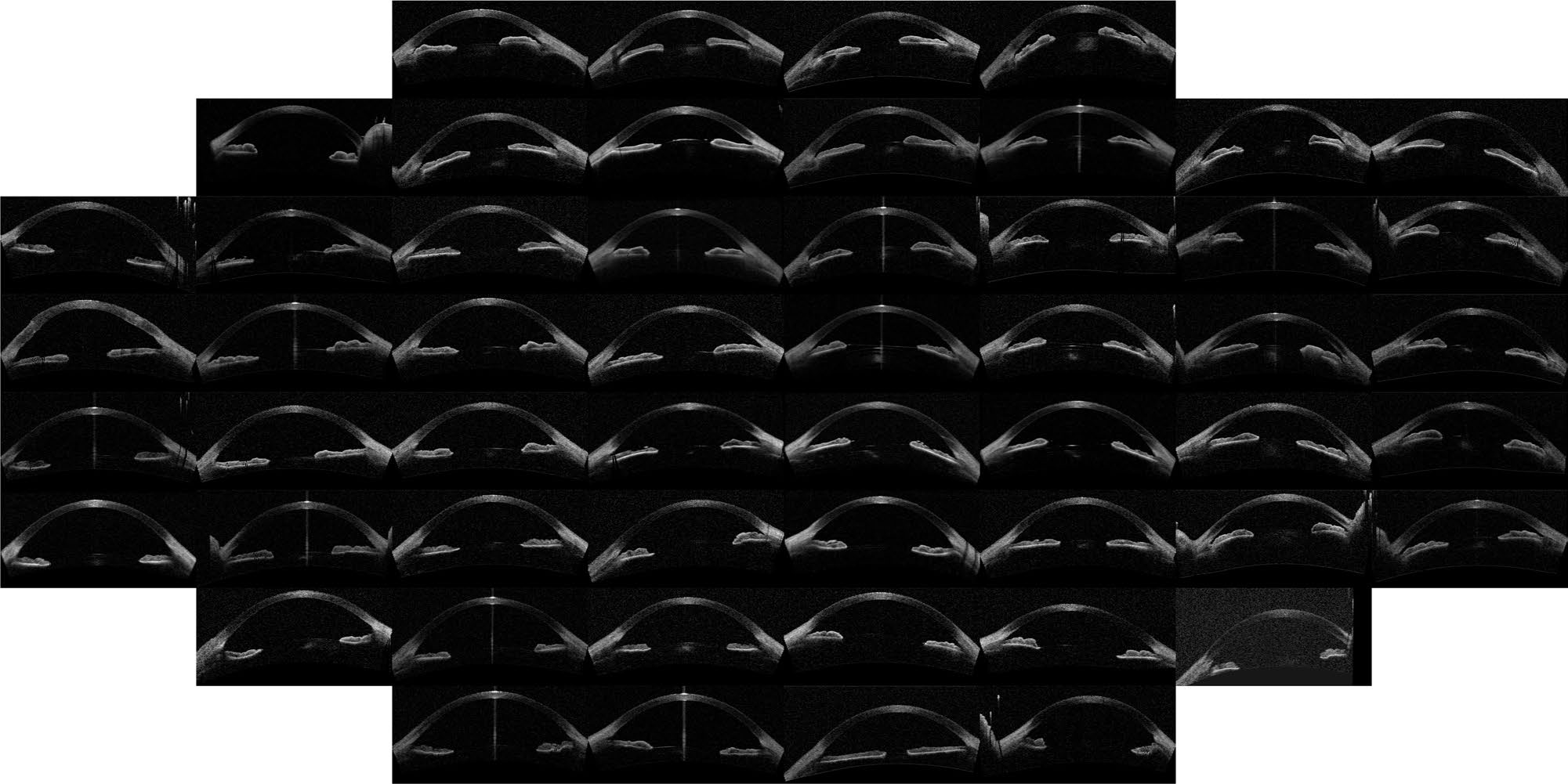
In Fig. 5 the features returned by the unsupervised algorithm, using t-SNE, are compared with the features obtained from the manual annotation of the images: in the left panel the color code indicates the chamber depth, and in the right panel, it indicates the mean angle (average of α and β) of each annotated image. Clearly, the features obtained from the manual annotation correlate very well with the features returned by the unsupervised algorithm. However, one should notice that the annotated features are not independent, but strongly correlated with each other. Finally, the manual classification done by two expert ophthalmologists is included in the t-SNE (w, v) map.
Desired business relationship
Patent licensing
Joint ventures
Technology development
New technology applications
Adaptation of technology to other markets
Current development status
Commercially available technologies
Intellectual property status
Patent already applied for
Patent application number :
Where :
Patent already applied for
Patent application number :
Where : Wordwide
The Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - BarcelonaTech is a public institution dedicated to higher education and research in the fields of engineering, architecture and science, which contributes its knowledge and expertise in order to increase scientific output, transfer its results to society and provide a network of scientific and technical state-of-the-art facilities and technology valorization services that place us at the leading edge of innovation and economic development.
The UPC has established itself as a driver of innovation and is the technology partner of choice for companies and organizations with which it develops projects and builds partnerships. A role borne out by the numerous agreements and research projects that have been set in motion by groups, organizations and laboratories; the creation of new technology-based companies; the generation and exploitation of patents, and the scientific and technical services UPC makes available to its environment in order to generate progress and employment.
The Technology Transfer Office (SGI) is responsible of Designing, coordinating and implementing research valorisation strategies, carrying out the protection policy of the research results, marketing these results through license contracts and designing and setting up the University's enterprise creation model in order to transfer the results of the research to the market, protect and commercialize these results, promote the culture of entrepreneurship and innovation, and create technology-based companies within the UPC environment.
Create your free account to connect with Servei de Gestió de la Innovació and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
Send a request for information
to Servei
Technology Offers on Innoget are directly posted
and managed by its members as well as evaluation of requests for information. Innoget is the trusted open innovation and science network aimed at directly connect industry needs with professionals online.
Need help requesting additional information or have questions regarding this Technology Offer?
Contact Innoget support