Never miss an update from Universidad de Alicante
Create your free account to connect with Universidad de Alicante and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
The Applied Electrochemistry and Electrocatalysis research group at the University of Alicante has developed a device for desalinating food products based on the electrodialysis technique.The application of an electric field to the device containing the food product to be desalinated causes and allows the movement of the sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions contained in the product, leaving the product desalinated, considerably shortening both desalination time and water consumption, compared to other more common methods.The device, which is protected by a patent application, has been developed on a laboratory scale using salted cod as a food product. The research group is currently developing a prototype to be applied in the hotel and catering industry.Companies interested in the commercial exploitation of the technology are being sought.
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
The Applied Electrochemistry and Electrocatalysis research group of the University of Alicante has developed a device to desalinate a solid salted food product based on the application of the electrodialysis technique.
The device consists of four compartments linked in series between which are arranged ion exchange membranes (Figure 1):
1. CATHOLYTE: A compartment containing a solution of at least one salt and/or inorganic acid, compatible with food use. The first electrode, more specifically the cathode, is immersed in it;
2. DILUATE: A compartment containing one or more pieces of foodstuff salted in water;
3. CONCENTRATE: a compartment containing a sodium chloride solution;
4. ANOLYTE: A compartment containing a solution of an inorganic anion and an inorganic cation compatible with food use, with a second electrode immersed in this second solution, more specifically the anode.
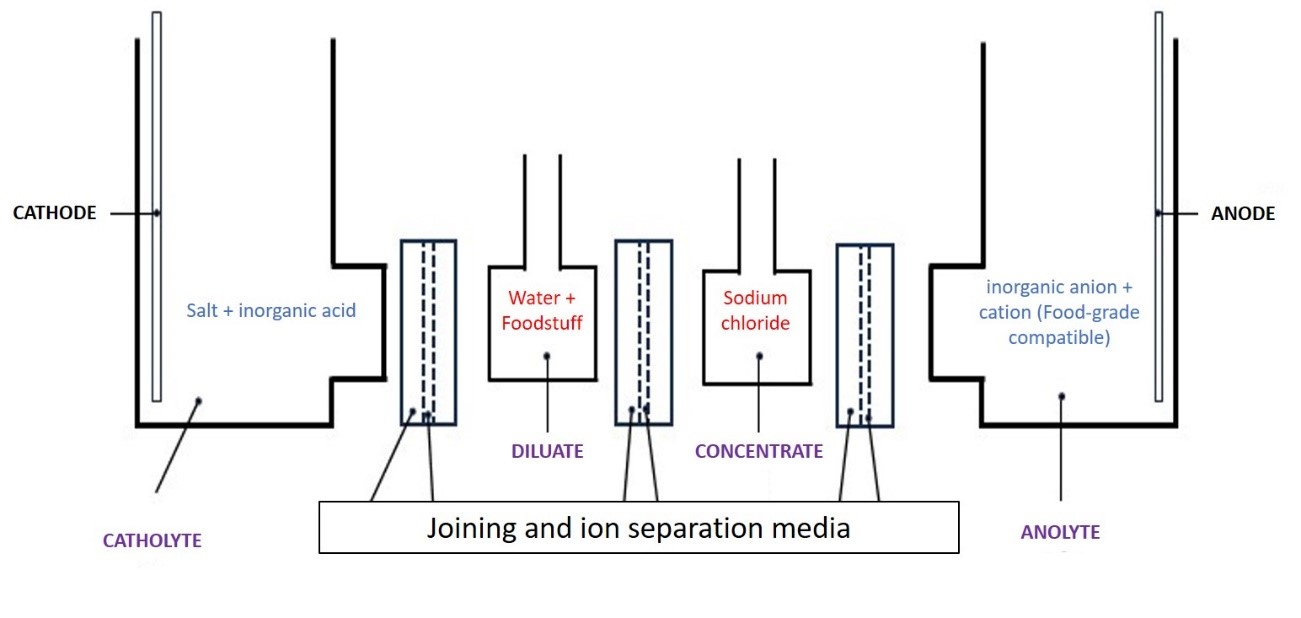
Figure 1. Schematic of a front view of the device.
To carry out the desalination of the food product by electrodialysis, a piece of the food product is first introduced into the DILUATE. An electric field is then applied between the two electrodes of the device. This current flow between the electrodes triggers the following processes:
• oxidation of water to oxygen at the anode (2H2O ---> O2 + 4H+ + 4e-);
• hydrogen formation at the cathode (2H+ + 2e- ---> H2)
• migration of the ions presents in the different solutions : the anions and cations presents in the DILUATE compartment, which come from the salted food product, travel through the ion exchange membranes towards the CONCENTRATE compartment and the CATHOLYTE compartment, leaving a desalinated solution in the DILUATE compartment.
More specifically:
• the anions present in the DILUATE are transported to the anode;
• the cations present in the DILUATE are transported towards the cathode;
• the ion exchange membranes cause the ions (anions and cations) to migrate from the DILUATE causing the solution in the DILUATE to lose salinity and also desalting the food product by forcing the chloride (Cl-) and sodium (Na+) ions out of the food product into the solution
• Simultaneously, the CONCENTRATE gains salinity.
Given the low value of the current density that is circulated, the amount of gases generated is very low and there is no significant risk in the handling of the device.
By circulating a direct electric current, the time of process and the intensity of the current are related to the amount of salt that is removed from the food and therefore allow to choose the desired degree of desalination. The nature and low value of the electric current does not alter the quality of the desalinated product.
The desalination time is variable as it depends on several factors, such as: size of the food product, thickness of the food product, percentage or degree of desalination to be achieved for a culinary application.
TECHNOLOGY ADVANTAGES AND INNOVATIVE ASPECTS
TECHNOLOGY ADVANTAGES
The device developed by researchers at the University of Alicante to desalinate food products has the following advantages:
• It makes it possible to desalinate a salted food product, using a quantity of water that is normally less than that used in conventional processes and in a much shorter time.
• It avoids having to replace the water periodically or to be continuously adding water.
• It allows the desalination time to be selected, which is directly related to the percentage or degree of desalination to be achieved for the desired culinary application. Therefore, there is greater control over the degree of salt to be obtained.
• The application of this technique does not affect either the texture or the quality of the treated food product.
• The device is easily scalable, being able to adapt its configuration for industrial applications as well as for small household appliances for catering.
• The DILUATE compartment is modular.
INNOVATIVE ASPECTS
The main innovative aspect of this technology is the application of the electrodialysis technique to desalinate solid salted food products.
CURRENT STATE OF DEVELOPMENT
The technology has been developed at laboratory scale using salted cod as the food product to be desalinated.
Using two different conditions, the researchers obtained the following results:
• Applying a controlled current intensity of 100 mA, for a time of 120 minutes they achieved a degree of desalination of 96 % over the initial salt content of the cod piece.
• By applying a controlled potential difference of 15 V for a time of 60 minutes, they achieved a degree of desalination of 66 % of the initial salt content of the cod piece.
The research group is currently working on the development of a prototype for a restaurant. This prototype can be used to desalinate a cod loin in 4 pieces of 250 g each.
COLLABORATION SOUGHT
Companies interested in acquiring this technology for commercial exploitation are sought:
• Patent licensing agreements.
• R&D projects.
• Development projects to adapt them to the needs of the interested party.
• Proof of concept projects, etc.
Company profile sought:
• Companies manufacturing industrial machinery for the food sector.
• Companies manufacturing electrical appliances for the restaurant and catering sector.
Ahead of the current Coronavirus outbreak, Innoget is fully committed to contributing to mobilizing scientific and expert communities to find a real solution to the Covid-19 pandemic. Therefore, we're supporting worldwide calls and programs that could help in any aspects of the coronavirus crisis.
Is your organization promoting or looking for innovation or research initiatives to mitigate the Covid-19 outbreak? Email us at covid19@innoget.com to list them.
Channeled through Innoget's online open innovation network, initiatives in the health, virology, medicine, or novel technologies applied to human health, among others, are listed and disseminated to Innoget members -ranging from hospitals, research institutes, scientists, businesses, and public administrations- and innovation partners worldwide.
Create your free account to connect with Universidad de Alicante and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
Send a request for information
to Universidad de Alicante
Technology Offers on Innoget are directly posted
and managed by its members as well as evaluation of requests for information. Innoget is the trusted open innovation and science network aimed at directly connect industry needs with professionals online.
Need help requesting additional information or have questions regarding this Technology Offer?
Contact Innoget support