Never miss an update from Universidad de Alicante
Create your free account to connect with Universidad de Alicante and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
The Plant Proteomics and Functional Genomics group of the University of Alicante, in collaboration with the Institute of Integrative Systems Biology of the University of Valencia, has developed the technology of plant cell cultures of the genus Morus to obtain stilbenes. The innovation lies in the simultaneous use of two elicitor compounds to promote their production. With this technology, trans-resveratrol and trans-oxyresveratrol are obtained in high quantities, with the possibility of using them in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries thanks to their powerful antioxidant character. Companies interested in acquiring this technology for its commercial exploitation through patent licensing agreements are sought.
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
In order to solve the biotechnological problems described above, it is necessary to have a more efficient method for obtaining t-oxyresveratrol in a single process.
In this sense, a method has been developed to obtain stilbenes by the combined addition of cyclodextrins and methyl-jasmonate to a culture medium of plant cells of the genus Morus. Specifically, large extracellular quantities of t-reveratrol and, above all, t-oxyresveratrol are obtained (see Figure 1):
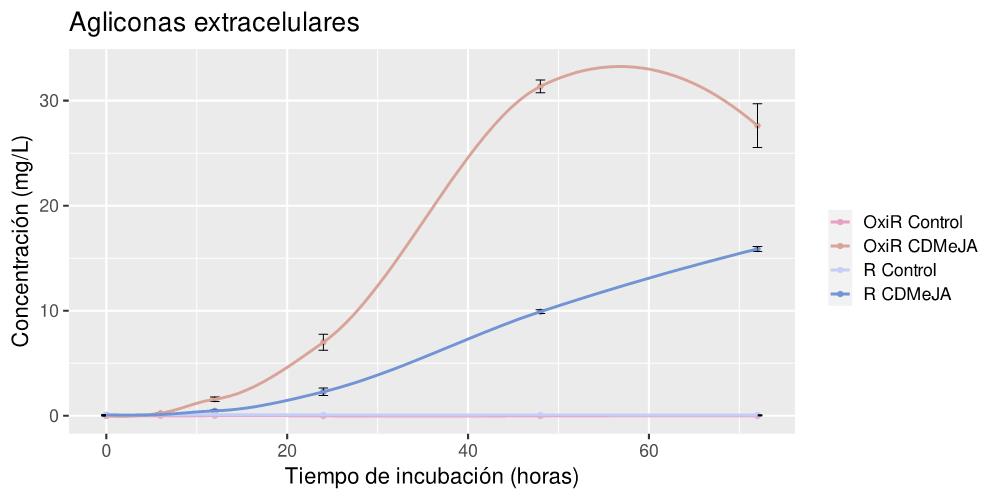
Figure 1: Kinetics of extracellular accumulation of the aglycone (non-glycosylated) forms of t-resveratrol and t-oxyresveratrol in milligrams per litre of extracellular medium, from a cell culture of Morus alba red clone elicited with the combination of cyclodextrins and methyl jasmonate, versus untreated control.
Any cell line of a plant of the genus Morus is capable of producing these compounds, either naturally or after genetic modification.
The method of production comprises the following steps:
1) Addition of cyclodextrins and methyl-jasmonate to a culture medium of plant cells of the genus Morus.
2) Incubation of the cell culture medium obtained in the previous step.
3) Separation of t-resveratrol and t-oxyresveratrol (obtained in step 2) from the culture medium.
4) Purification of the t-resveratrol and t-oxyresveratrol separated in the previous step.
Some images of the blackberry plant cells obtained can be seen below:

Picture 1: Development of the growth of mulberry plant cells ("white" and "red" clones) from the solid state to the state in liquid suspension. The name "red" clone is due to the color of the fruits of the specimen from which it originates (the plant cells of both clones, "white" and "red", have the same color).
TECHNOLOGY ADVANTAGES AND INNOVATIVE ASPECTS
ADVANTAGES OF THE TECHNOLOGY
The developed method has the following advantages:
1) It is more efficient than current biotechnological methods.
2) It is carried out in a single process, which simplifies the production process.
3) The accumulation of t-resveratrol and t-oxyresveratrol is mostly extracellular.
4) The extraction and purification process is simplified (no need to break the plant cells and then remove the cellular remains).
5) It is possible to use the plant cells in suspension for new t-resveratrol and t-oxysveratrol synthesis cycles.
6) The trans- forms of both compounds (which are the biologically active forms, as opposed to the cis- isomers) are mainly generated.
7) High amounts of stilbenes are obtained:
• In the red clone:
º 124 mg/L t-oxyresveratrol.
º 24 mg/L t-resveratrol.
• In the white clone:
º 114 mg/L t-resveratrol.
º 81 mg/L de t-oxyresveratrol.
8) t-Oxyresveratrol and t-resveratrol production is stable and independent of environmental and socio-economic factors.
9) The quality of the final product is improved.
10) The process is sustainable and environmentally friendly.
11) The technology allows large quantities of stilbenes to be obtained at a lower cost than other similar techniques currently available on the market, which increases its accessibility for different industrial applications.
INNOVATIVE ASPECTS OF THE TECHNOLOGY
Surprisingly and unexpectedly, the combined use of cyclodextrins and methyl jasmonate in plant cell cultures of the genus Morus results in the production of two stilbenes not anticipated in the state of the art, namely t-resveratrol and, especially, t-oxyresveratrol.
The cumulative concentrations of both stilbenes are higher in the combined treatment than the sum of the individual treatments, hence the synergistic effect of both elicitors.
The accumulation of both stilbenes occurs mostly in the extracellular medium, which simplifies the extraction and purification process and reduces production costs.
The technology makes it possible to obtain large quantities of t-resveratrol and, above all, t-oxyresveratrol.
CURRENT STATE OF DEVELOPMENT
The described technology has been developed at laboratory scale (Technology Readiness Levels: TRL = 4).
Laboratory tests have shown the synergistic effect of the use of methyl jasmonate and different types of cyclodextrins on the production of t-resveratrol and t-oxyresveratrol in mulberry cell cultures.
When Morus Alba cell culture is elicited with methylated (or randomly hydroxypropylated) cyclodextrins, an extracellular accumulation of:
t-Resveratrol:
• 60-140 times higher (in the white clone) compared to the control.
• 30-60 times higher (in the red clone) compared to the control.
t-Oxyresveratrol:
• 600-800 times higher (in the red clone) than the control.
• 30-60 times higher (in the white clone) than the control.
And when the cell culture is elicited with the combination of cyclodextrins and methyl jasmonate, an additional extracellular accumulation of t-resveratrol and t-oxyresveratrol is 3 times higher, compared to the sum of the levels accumulated in the single treatments, hence the synergistic effect of the joint elicitation (both in the white and red clones).
The glycosylated forms inside the cells do not change significantly over time due to elicitation, whereas the aglycones (non-glycosylated forms), both intracellular and extracellular, exhibit a cumulative pattern over time. This change is more intense for t-oxyresveratrol than for t-resveratrol in the case of the red clone cell line.
COLLABORATION SOUGHT
Companies interested in acquiring this technology for commercial exploitation through patent licensing agreements are sought.
Ahead of the current Coronavirus outbreak, Innoget is fully committed to contributing to mobilizing scientific and expert communities to find a real solution to the Covid-19 pandemic. Therefore, we're supporting worldwide calls and programs that could help in any aspects of the coronavirus crisis.
Is your organization promoting or looking for innovation or research initiatives to mitigate the Covid-19 outbreak? Email us at covid19@innoget.com to list them.
Channeled through Innoget's online open innovation network, initiatives in the health, virology, medicine, or novel technologies applied to human health, among others, are listed and disseminated to Innoget members -ranging from hospitals, research institutes, scientists, businesses, and public administrations- and innovation partners worldwide.
Create your free account to connect with Universidad de Alicante and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
Send a request for information
to Universidad de Alicante
Technology Offers on Innoget are directly posted
and managed by its members as well as evaluation of requests for information. Innoget is the trusted open innovation and science network aimed at directly connect industry needs with professionals online.
Need help requesting additional information or have questions regarding this Technology Offer?
Contact Innoget support