Generation of hydrogen with reduced energy input
Hydrogen can be produced through water electrolysis while avoiding the generation of polluting byproducts Water electrolysis is currently the most common method to obtain hydrogen, which is regarded as the fuel of the future due to its clean combustion (without CO 2 emission). In order to support the energy transition there is a need for high efficiency and low cost methods to produce hydrogen.
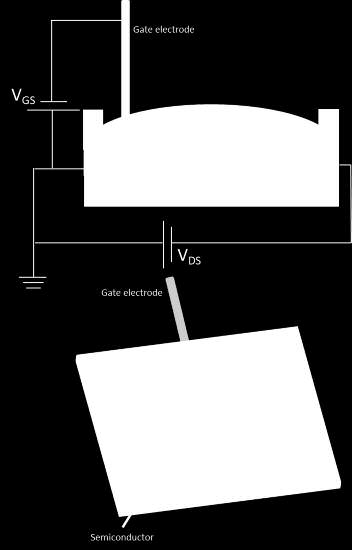
By introducing a new method to structure the electrodes, this invention reduces the voltage difference that is needed for the reaction while maximizes the concentration of the electric field in areas apart from the surface of the electrodes. This facilitates the electrolysis reaction while allowing the use of thinner electrodes without compromising its resistance or durability. Furthermore, the method can work with electrodes in multiple shapes and structures, so can be adapted to any required specifications.
Main innovations and advantages
· Facilitates the reactions of electrolysis by reducing the required voltage input.
· Avoids overcharging the surface of the electrodes by redirecting electric charges to other areas, improving their resistance.
· The structure of the electrodes can be easily adapted to any application requirements.
· Its main field of application is the water electrolysis for the generation of hydrogen gas, that can be used as a clean CO 2-free fuel.
· Other possible fields of application include: the deposition of atoms in surfaces or layers, the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to methanol, or the chemical synthesis of a variety of molecules.