Method that allows the transformation of low-temperature coke (green coke) into graphene without any graphitization treatment, using the chemical route. This is a sustainable and effective process that takes advantage of a by-product of the petrochemical industry, coke, which is processed at considerably lower temperatures than those used in the usual processes for obtaining graphene materials and without the risks associated with them.
Industrial partners from petrochemical or carbochemical sectors are being sought to collaborate through a patent licence agreement.
An offer for Patent Licensing
An alternative to conventional methods
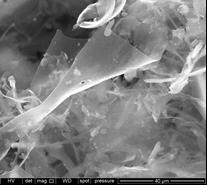
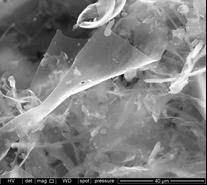
SEM image of a graphene obtained by thermal reduction up to 1000ºC of graphene oxide prepared according to the procedure described in this patent Coke is a by-product of the petrochemical and carbochemical industry that can be used as an alternative to graphite to produce graphene. Its processing for this purpose requires its prior graphitization, process that consists of a heat treatment at around 3000ºC to promote its crystalline arrangement. Green cokes, which are cokes obtained at low temperatures and, therefore, with low crystalline ordering, can be processed to prepare graphene materials by chemical methods. However, its processing carries risks due to its high reactivity, even causing deflagrations in some cases.
CSIC researchers have developed a sustainable and safe process to produce graphene. Said process uses green coke as starting material. The chemical route is used herein, but without the need for the previous graphitization of the green coke, which allows working at temperatures that do not exceed 1000ºC. Experimentally, it has been shown that it is a safe method that avoids the usual risks associated with the processing of green cokes.
Main innovations and advantages
- It is a more sustainable method since it does not require heat treatmentsat high temperatures.
- It is a safe method that avoids the risk associated with the processing of green cokes through the traditional chemical route.
- It is a scalable method that uses reagents commonly used in the industry.
- The applications of the final graphene materials include many sectors such as image, energy, electronics, etc. The obtained materials can beused even in emerging applications.)