Technology Offers Site map description
N
UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS posted this:
New methodology for the catalytic reduction of nitroaromatic compounds environmental friendlyThe invention relates to a new general method for the reduction of nitroarenes to anilines using a Mo(VI) catalyst and pinacol as reducing agent. The products obtained show excellent yields. It should be noted that this new method uses an easily available and non-toxic reducing agent that generates non-toxic byproducts which are easily separated from the amine synthesized.UNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS posted this:
New methods for the detection and discrimination of contaminants and organic metabolites of high environmental impact by means of fluorogenic probesThe research group develops new selective fluorogenic probes for organic molecules of low molecular weight and high social and environmental impact. The newly developed fluorogenic probes are able of show large differences of fluorescence in the presence of certain analytes and they are oriented to the resolution of detection problems for contaminants of high environmental impact for which a satisfactory solution does not exist, such as phosphorylating reagents from chemical weapons, methylmercury, cyanide ion, doping substances and recreational abuse drugs. By incorporation of the fluorogenic probes to silica nanomaterials, the research group generates new luminescent sensory materials of toxicological and environmental utility.Universitat de Lleida posted this:
New microbial culture to control foodborne pathogens in fresh-cut fruitA new solution based on a microbial culture capable of inhibiting the growth of foodborne human pathogens such as Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli in fresh-cut fruit. New microbial culture with demonstrated bio-preservative activity. The use of the proposed technology in the fresh-cut fruit industry prevents the development of food-borne pathogens, ensures food safety and maintains the product quality throughout the product shelf-life. This technology is complementary to existing preventive methods. CNIC (TTO)Spanish National Center for Cardiovascular Research (CNIC)CNIC (TTO)
CNIC (TTO)Spanish National Center for Cardiovascular Research (CNIC)CNIC (TTO)Technology Transfer Office at Spanish National Center for Cardiovascular Research (CNIC)
View ProfileCNIC (TTO) posted this:
New microRNAs for the diagnosis of cardiomyopathiesInflammation in the myocardium or myocarditis is a disease with heterogeneous aetiology, frequently caused by an infectious pathogen, toxins, drugs or by an autoimmune disorder. Its clinical variability and its nonspecific symptoms make the diagnosis of myocarditis a process that is not always easy. There is an urgent need for accurate, fast point-of-care tests that simultaneously provide diagnostic and prognostic information about a patient entering the hospital with symptoms of acute heart failure. CNIC researchers have identified the role of an specific miRNA in cardiomyopathies processes and have studied the differential expression in blood plasma of patients compared with healthy subjects. These miRNAs can be used as biomarker to improve the diagnosis of acute myocarditis.
Technology Transfer Office at Spanish National Center for Cardiovascular Research (CNIC)Javier Montiel Bonmatí posted this:
New multifunctional material for catalysis applicationsThe "Advanced Materials" research group at the University of Alicante has developed a foamed material comprising three phases: a structural matrix, at least one host phase, and a fluid. This material is characterized by the fact that the structural matrix comprises a plurality of interconnected porous cavities, the host phase(s) is/are housed within at least one porous cavity of the structural matrix and the fluid is housed within the porous cavities. The host phase(s) is/are housed within the porous cavities of the structural matrix without maintaining any bond with the latter. The structural matrix may consist of a material of a metallic, polymeric or ceramic nature or mixtures thereof. Meanwhile, the host phase(s) is/are a functional material, the fluid being a liquid or a gas. These materials have many potential uses, among which one is as a catalyst material or as a support for catalysts. Companies interested in the commercial exploitation of this material are sought through a patent license agreement.
Universidad de AlicanteJavier Montiel Bonmatí posted this:
New multifunctional material for controlled-drug-release implantsThe "Advanced Materials" research group at the University of Alicante has developed a foamed material comprising three phases: a structural matrix, at least one host phase, and a fluid. This material is characterized by the fact that the structural matrix comprises a plurality of interconnected porous cavities, the host phase(s) is/are housed within at least one porous cavity of the structural matrix and the fluid is housed within the porous cavities. The host phase(s) can be housed within the porous cavities of the structural matrix without maintaining any union or maintaining discrete unions with the latter. The structural matrix may consist of a material of a metallic, polymeric, ceramic nature or mixtures thereof. Meanwhile, the host phase(s) is/are a functional material, the fluid being a liquid or a gas. These materials have many potential uses, among which ones is as an implant material, with the additional possibility of exerting a controlled release of drugs. Companies interested in commercial exploitation of this material through a patent license agreement are sought.
Universidad de AlicanteJordi Reverter posted this:
New Nanoporous Graphene materialA bottom up unique method build the holy graphene from molecular blocks. The molecular blocks used define the size and shape of the pores, which are identical with atomic precision. We can also control the chemical functionalization of the material. This material has semiconducting properties with a bandgap similar to Si, opening new applications for graphene-based materials. This new material can be used for sieving, sensing, (opto)electronics or its combinations.
Licensing Manager at Institut Català de Nanociència i NanotecnologiaUniversidad de Cádiz posted this:
New nanostructured catalyzers without noble metals and with low content in lanthanidesSince the 1990's, the mixed oxides of cerium and zirconium have replaced cerium oxide in the composition of the three-way catalyzers used in the automotive industry. The fundamental reason for this is the improved textural behaviour of the oxides of Ce/Zr, compared with the effectiveness of cerium oxide. These mixed oxides are also more effective in the exchange of oxygen with the medium. The Oxygen Storage Capacity (OSC) of the compound is therefore the key property for its application as a component in catalyzers. However, the rare earth metals which are the critical component of these catalyzers have currently increased considerably in price, due to greater demand and limited supply from the few exporting countries. The research group working in this field has been able to obtain nanostructured oxides of Ce/Zr and Ce/Zr/Y with low content in Ce that present very good oxygen storage properties. In addition, costly noble metals are not employed in their formulation, which represents an important economic advantage.Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC posted this:
New nanostructured material for tissue regenerationA new ion release system for revascularization and tissue regeneration based of calcium phosphate glass nanoparticles has been patented and developed. Partners to further develop the technology and/or to establish commercial agreements along with technical cooperation are sought.OTRI-Universidad de Málaga posted this:
New nanosystem to be applied over white adipose tissueThis invention is developed by the University of Málaga (UMA) in collaboration with Andalusian Public Health System and CIBER. They have developed a new nanosystem to be applied over white adipose tissue. This nanosystem changes white fat into brown fat.
Technology Transfer Office (TTO) at Universidad de MálagaJavier Montiel Bonmatí posted this:
New noble metal-free catalyst for the production of propylene oxideThe Institute of Materials of the University of Alicante has developed a new and cost-effective catalyst without noble metals to obtain propylene oxide from the selective oxidation of propylene. The catalytic system is characterized by not making use of dangerous or highly contaminating agents, and by not producing high quantities of reaction by-products. In addition, it shows a high selectivity towards propylene epoxide in the selective oxidation of propylene. Companies interested in acquiring this technology for commercial exploitation are sought.
Universidad de AlicanteUniversity of Vigo posted this:
New non-destructive method for “in situ” monitoring of anticorrosive protection of organic coatingsPaint coating is one of the most used methods to delay corrosion process in metallic structures. Metal corrosion is the main reason of metallic infrastructure deterioration (bridges, boats, planes…) causing failures in numerous industrial areas. The economic loss due to corrosion is estimated at about 4% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in industrialized countries. Due to the serious consequences of this phenomenon, it is essential to develop effective methods for early detection of coatings failures and establishment of deterioration mechanisms. However nowadays, most of the inspection methods are indirect, destructive and based on deterministic or probabilistic models, which limits the coatings performance assessment on the in real operating conditions. The Corrosion Engineering and Materials Research Group (ENCOMAT) proposes a solution to this problem with a new device and a direct and non-destructive test based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The main novelty of the device and procedure is the new portable sensor adaptable to any surface. The device, fixable by vacuum to the surface under study, makes possible the measurement of the electrochemical interfacial impedance. That is the main parameter of interest for adherence quality and anti-corrosion performance. The procedure reduces testing time and allows in situ assays to be performed. Innovative aspects and advantagesUniversity of Vigo posted this:
New non-destructive method for “in situ” monitoring of anticorrosive protection of organic coatingsPaint coating is one of the most used methods to delay corrosion process in metallic structures. Metal corrosion is the main reason of metallic infrastructure deterioration (bridges, boats, planes…) causing failures in numerous industrial areas. The economic loss due to corrosion is estimated at about 4% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in industrialized countries. Due to the serious consequences of this phenomenon, it is essential to develop effective methods for early detection of coatings failures and establishment of deterioration mechanisms. However nowadays, most of the inspection methods are indirect, destructive and based on deterministic or probabilistic models, which limits the coatings performance assessment on the in real operating conditions. The Corrosion Engineering and Materials Research Group (ENCOMAT) proposes a solution to this problem with a new device and a direct and non-destructive test based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The main novelty of the device and procedure is the new portable sensor adaptable to any surface. The device, fixable by vacuum to the surface under study, makes possible the measurement of the electrochemical interfacial impedance. That is the main parameter of interest for adherence quality and anti-corrosion performance. The procedure reduces testing time and allows in situ assays to be performed.University of Vigo posted this:
New non-destructive method for “in situ” monitoring of anticorrosive protection of organic coatingsThe main novelty of the device and procedure is the new portable sensor adaptable to virtually any surface. The device, fixable by vacuum to the surface under study, makes possible the measurement of the electrochemical interfacial impedance, that is the main parameter of interest for adherence quality and anti-corrosion performance.University of Vigo posted this:
New non-destructive method for “in situ” monitoring of anticorrosive protection of organic coatings Authors: Xosé Ramón Nóvoa and Carmen Pérez.Paint coating is one of the most used methods to delay corrosion process in metallic structures. Metal corrosion is the main reason of metallic infrastructure deterioration (bridges, boats, planes…) causing failures in numerous industrial areas. The economic loss due to corrosion is estimated at about 4% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in industrialized countries. Due to the serious consequences of this phenomenon, it is essential to develop effective methods for early detection of coatings failures and establishment of deterioration mechanisms. However nowadays, most of the inspection methods are indirect, destructive and based on deterministic or probabilistic models, which limits the coatings performance assessment on the in real operating conditions. The Corrosion Engineering and Materials Research Group (ENCOMAT) proposes a solution to this problem with a new device and a direct and non-destructive test based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The main novelty of the device and procedure is the new portable sensor adaptable to any surface. The device, fixable by vacuum to the surface under study, makes possible the measurement of the electrochemical interfacial impedance. That is the main parameter of interest for adherence quality and anti-corrosion performance. The procedure reduces testing time and allows in situ assays to be performed. Innovative aspects and advantagesUniversidad de Alcalá-OTRI posted this:
New organo-metallic catalysts for the manufacture of polymersA research group from the Inorganic Chemistry Department of Alcalá University has developed a technology that presents a range of catalysts based on coordination complexes and organometallic, active in functionalization processes (expoditation, hydrosilylation) and polymerization of different organic substrates (olefins and cyclic esters). They are metal complexes belonging to the first transition groups (groups 4-6) and elements from the main groups (groups 1,2 and 13). Its application is aimed at the synthesis of materials with new properties (silicon polymers, biodegradable plastics, polyesters) and the production of small molecules with high added value, used as starting products in many industrial processes (epoxides, silanes). The group is looking for manufacturing agreements and joint venture agreements with companies from the agrofood industry, construction and petrochemicals.Otava Research Institute posted this:
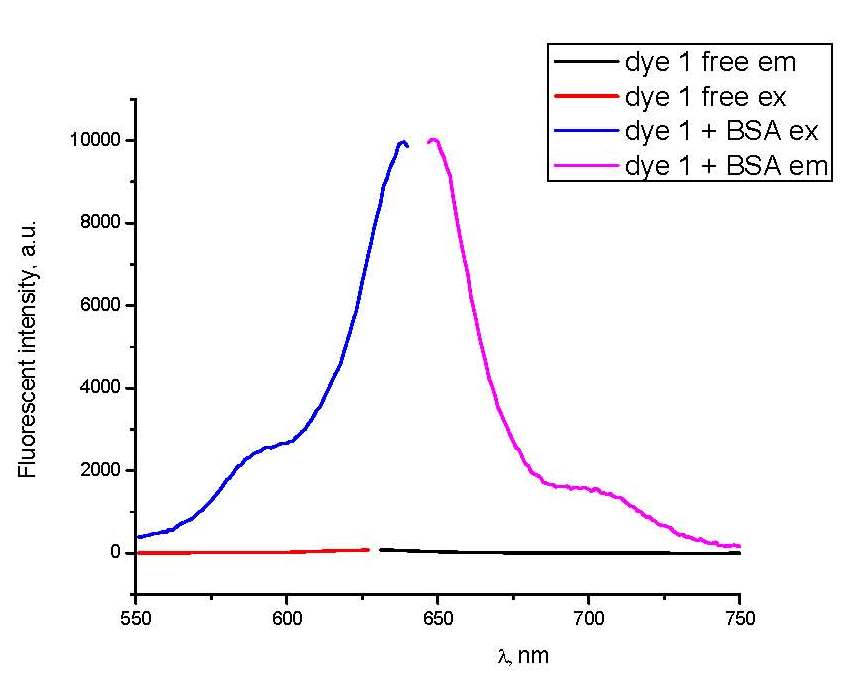
New Original Squaraine Dye for protein detectionUkrainian Laboratories represents the original new squaraine dye for the protein detection. The dye is already synthesized and ready to use for biomedical application. The dye has a significant increase in the fluorescence intensity in the presence of protein (123 times) and does not change its intensity in the presence of nucleic acids.Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC posted this:
New orthotic gloveNew orthotic glove designed to amplify hand strength . An actuated hand exoskeleton useful for old or disabled people who have not enough strength in their hands has been patented and developed.Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC posted this:
New orthotic glove designed to amplify hand strengthAn actuated hand exoskeleton useful for old or disabled people who have not enough strength in their hands has been patented and developed. This new technology allows amplification of hand-grasping force. Partners to further develop the device and/or to establish commercial agreements along with technical cooperation are sought.Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - UPC posted this:
New orthotic glove designed to amplify hand strength An actuated hand exoskeleton useful for old or disabled people who have not enough strength in their hands has been patented and developed. This new technology allows amplification of hand-grasping forcThe Challenge Partial hand disability represents a serious problem for many people, who although they have mobility and sensitivity in their hands, are not strong enough to hold a simple mug. For example, people with diseases, elderly or people who have suffered a traffic accident. In order to improve their quality of life, the design of devices such as the exoskeleton presented is so important. Currently, there are some similar devices nevertheless most of them need external energy and sophisticated drive mechanisms, complicating their use and maintenance.IMIM Institut Recerca Hospital del Mar posted this:
New phenolic natural extract obtained from olive and herbal spices with proven cardioprotective effect.This product consists of a natural extract wich combines olive oil phenols and other bioactive compounds from herbal species. The bioactive compounds of the natural extract have been characterized and quantified. Its use allows a novel therapeutic approach by means of the combination of complementary antioxidants from different origins that provides additional health benefits. Consumer acceptance has previously been assessed by conducting a panel test. Data from a randomized, controlled, crossover, clinical trial showed an improvement of vivo endothelial function and HDL subclass distribution, in humans. These effects were obtained with a low daily intake of the extract.University of Huelva posted this:
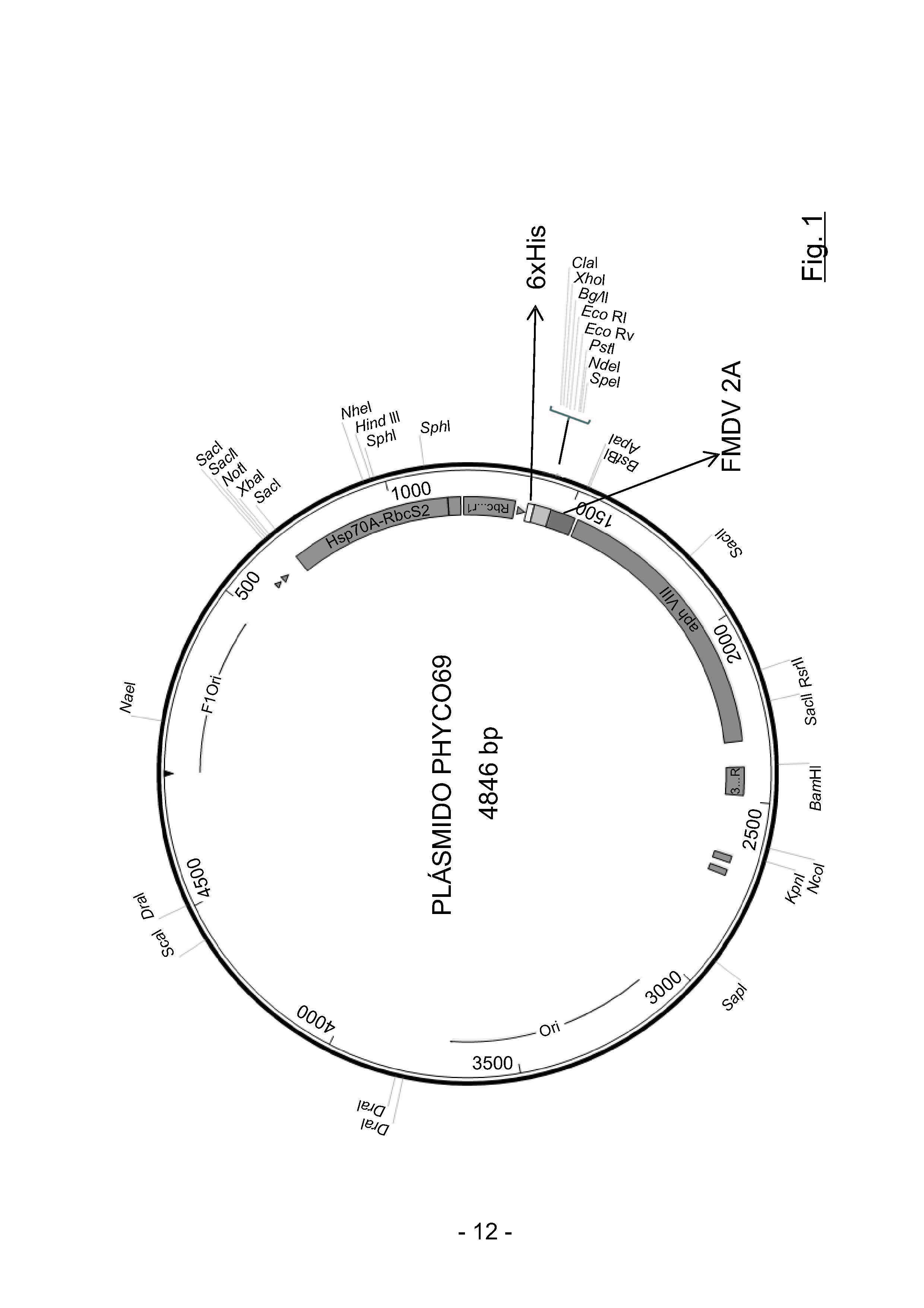
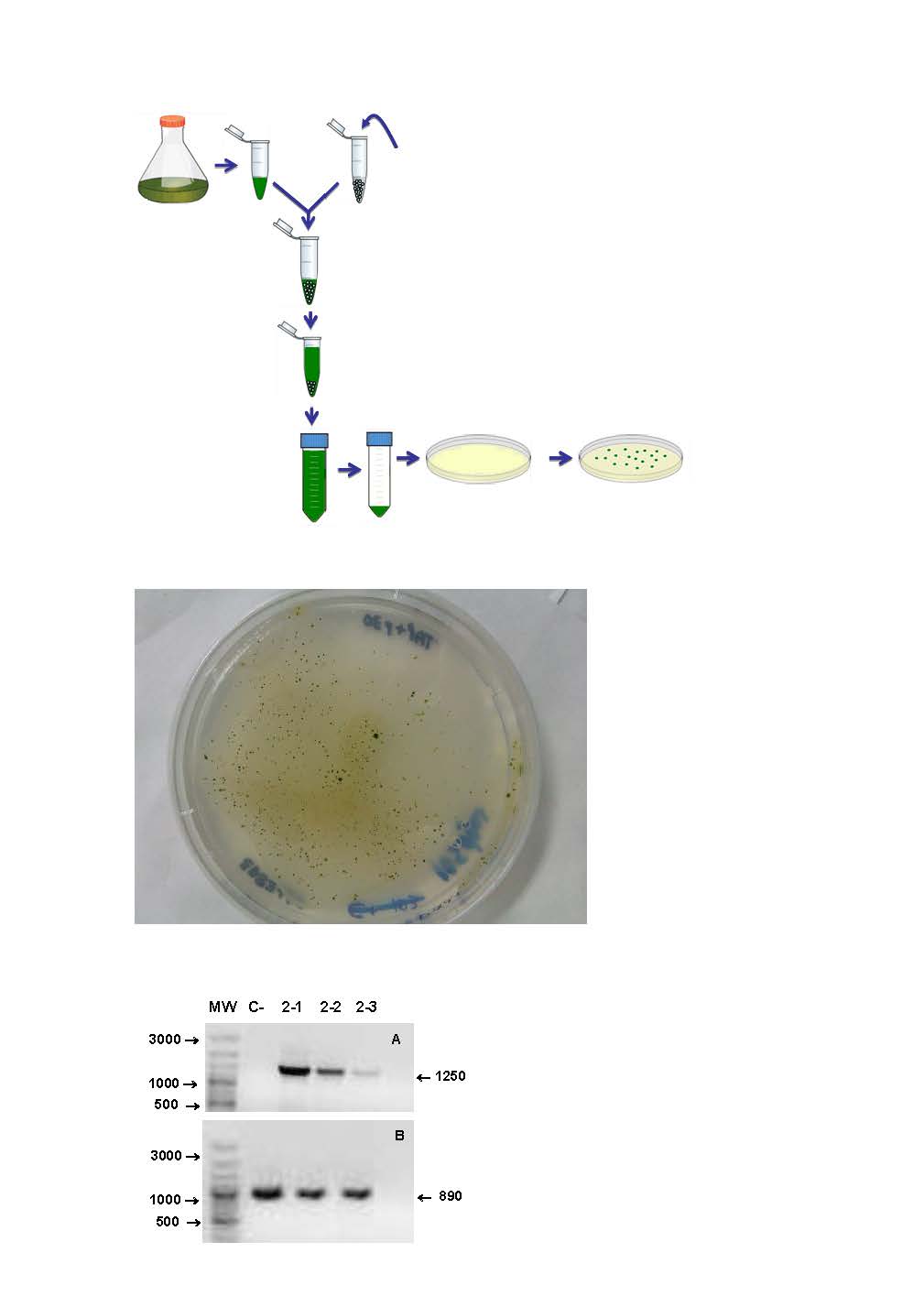
New plasmid and strategy for expression of exogenous proteins in eukaryotic microalgae by translational fusion with a selectable markerThis plasmid solves the problems of low efficiency and instability of transgenes in the genetic manipulation of microalgae, as well as offers a procedure for the expression of high amounts of the protein of interest and better transformation efficiencyUNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS posted this:
New polymeric materials with exceptional mechanical and thermal propertiesA research group at the University of Burgos (UBU) has developed new aromatic polyamides (aramids) models and polymeric materials reinforced with carbon nano-fillers, chemically functionalized previously with these polyamide models, constituting materials with exceptional mechanical and thermal properties.University of Huelva posted this:
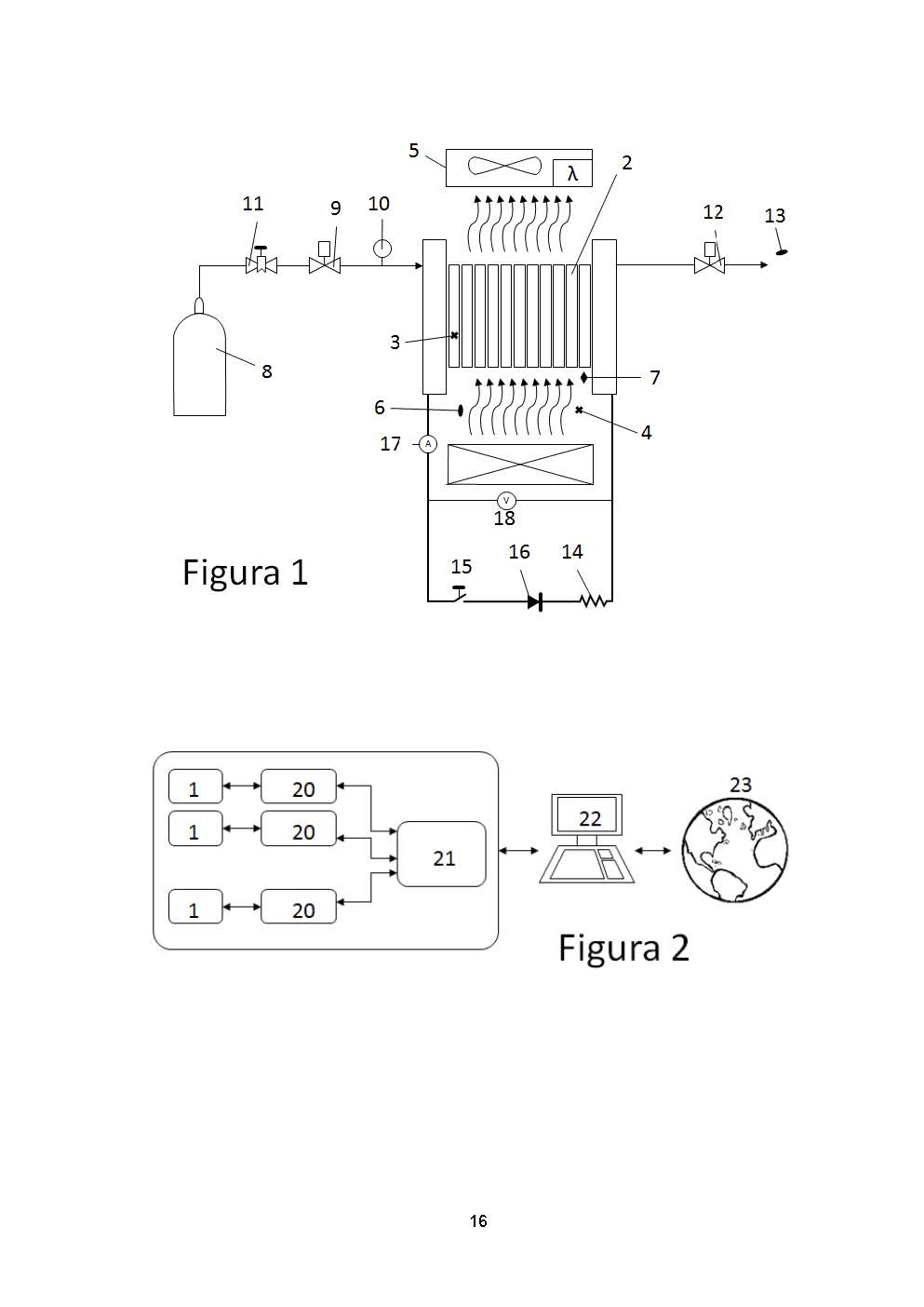
New power generation electric systemThe proposed system is characterized by the following aspects which make it unique: 1- The system is built from a number of PEM fuel cells, supplied by al least one hydrogen source. Each module include a monitoring and control subsystem, so it is possible to activate/deactivate module induividually. 2- Each module can supply a different power value. 3- The monitoring and control subsystem receives electrical signal from each modules like stack voltage, stack current and cell voltage. 4- The monitoring and control system has two levels: the first level aims to control each module (local control) and the second level is responsible for coordinate local controller. 5- The monitoring and control system is on-line accessible. 6- The control and monitoring system distributes homogeneously the operating hours between the modules when the power demand is lower than the maximum power. 7- Each module has a oxygenation/cooling subsystem which supplies oxygen to cathide and air for refrigerate the stack. 8- Each module has a hydrogen subsystem wich is the responsible for hydrogen delivery to stack at ambient pressure. 9- The hydrogen subsystem include a hydrogen purge line. 10- The Electric Power Generation System includes a simulator to reproduce the performance ogf the whole subsystem.University of Vigo posted this:
New prebiotics from biomass polysaccharides (hemicelluloses and pectins) for food and feedThe inventions describe optimized methods for producing purified non-digestible oligosaccharides with prebiotic properties suitable to be used as ingredients for functional foods or feed applications. Starting from a variety of raw materials containing hemicelluloses and/or pectins, the target compounds are obtained by hydrolytic reactions (in autocatalyzed aqueous media and/or in the presence of enzymes), and subjected to physicochemical refining processes to remove undesired byproducts. All the steps are based in sustainable and environmentally friendly technologies. The separation methods are scalable, and the final products show a high degree of purity. The ability of the purified oligosaccharide concentrates for causing prebiotic effects has been confirmed by in vitro experiments.Cracow University of Technology posted this:
New preparation method of silver nanoparticles suspension and silver nanoparticles suspension for medical, cosmetic and pharmaceutical application.Subject of this offer is the preparation method of silver nanoparticles suspension by reduction of silver salt by using reducing agent of natural origin and in the presence of a stabilizer. In this method, the following reducing agents are used apiproduct or extract of amber. The obtained nanoparticles can be applied in various industries, but the largest future is in the medical area, and as ingredient in cosmetic compositions due to the presence of non-toxic ingredients.Javier Montiel Bonmatí posted this:
New procedure for anoxic marine sediment remediationThe “Ecosystem and Biodiversity Management” (Spanish initials: GEB) and “Agricultural Chemistry” (Spanish initials: QA) research groups at the University of Alicante have developed a new anoxic marine sediment remediation system and procedure that allows in situ transformation of soft, black, muddy sediment with a high organic matter content and a characteristic fetid odour into well-oxygenated, firmer sediment that has a much lower organic matter content and is no longer black or foul smelling. The procedure involves injecting oxygen-saturated sea water into the sediment to displace anoxic pore water. A suction pump system collects sea water, which is then stored and treated in a tank by means of a bubbling system to achieve oxygen saturation before being injected via nozzles into the sediment to treat, using an injection sequence of between 90-180 minutes of rest and 50-70 minutes of injection. This technology, which has been developed at laboratory scale and is protected by patent application, could be used for remediation of anoxic sediments on shallow beaches and materials extracted during port dredging that require elimination of anoxic conditions. The research groups are seeking companies or public sector authorities interested in commercial exploitation of the invention.
Universidad de AlicanteUNIVERSIDAD DE BURGOS posted this:
New procedure for the aerobic oxidation of a sulfoxide group to a sulfone with significant improvements in its use and storageA new procedure for the oxidation of a sulfoxide group to a sulfone group has been patented. This new process consists in the oxidation of the sulfoxide with air in the presence of a molibdenum compound as catalyst, preferentially dioxomolibdenum (VI) bis(acetilacetonate) or dinuclear derivatives coming from its partial hydrolisis.Universidad de Cádiz posted this:
New procedure for the elimination of nutrients from waste waters by photobiotreatment with microalgasUCA researchers have developed a new process for the treatment of waste waters by using microalgae, specifically for the removal of nitrogen and phosphorus. This process is based on applying three fundamental findings made by the research group: • Before the microalgae start to grow, they are already consuming nitrogen and phosphorus when cultivated in waste waters. • The microalgae accumulate nutrients internally in such a way that the assimilation of nutrients commences before the growth phase, and at a rate that is considerably faster than the rate during the generation of biomass. • The initial elimination of nutrients prior to the growth of biomass takes place at a similar rate both in darkness and in the presence of light. To exploit this phenomenon, a procedure has been designed in which the two phases take place separately in two reactors: the first phase for elimination of nutrients from the waste water in darkness (known as ‘luxury uptake’) and the second for the growth of biomass under illumination. What this achieves is not only the efficient removal of the nutrients from the waste water but also, by means of a simple change of the mode of operation of the process, nutrients can be eliminated at night using the excess of biomass generated during daylight hours. To implement this advance, the research group has conceived a process for the separation of the biomass from the culture medium in both phases, by means of membrane technologies. The treatment plant can operate with cellular retention times very much longer than the hydraulic residence times. This, in turn, allows the same flow volumes of waste water to be treated in smaller reactors. • It enables waste waters to be treated at night without the need for a luminous phase. This cannot currently be done with the processes that employ existing photosynthetic organisms. • Simplicity of operation and reduction of costs in comparison with conventional technologies. It avoids the production of more solid residues, i.e. sludges, which require disposal. • The use of microalgae allows the treatment of waste waters with high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus but low content of organic matter (a characteristic of the waste waters of steelworks), since autotrophic organisms are involved. Thus the proposed process avoids the need to add organic matter from an external source, as is the case of other biological processes. • With the possibility of generating energy and capturing CO2, the biomass generated in the process represents value added in terms of energy consumption and environmental protectionUniversity of Huelva posted this:
New procedure for the genetic transformation of plant cells and kit for carrying out said methodThe strategy for transformation is extremely simple and does not involves subcloning the gene of interest in any vector. The kit is not based on specific promoters or regulatory DNA sequences, thus it can be applied to many different plant species, from unicellular microalgae to higher plant protoplasts. Since the strategy is not based on specific promoter or regulatory DNA sequences, only the marker and the gene of interest sequences are inserted in the microalgal genome, avoiding the introduction of undeserible DNA sequences in the transformant strain. This is very important given the concern that transfer of exogenous DNA through transgenesis causes in the public opinion